|
|
|
|
• WT-01 Components of human body |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
■ Vital unit, cell (structure, cell membrane, function of intracellular structure: membrane transport, energy yeilding, substance metabolism, cellular excitation) ■ Various organs maintaining life processes (various cells and their functional property - neuron, muscle cell, gland cell, epidermal cell, etc. - tissue - organ, organ system ) |
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
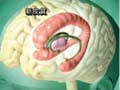
• WT-02 Acquisition of External Information and Psychiatric Function |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
■ Brain function -neural network, summary of cerebral function: processing of external information, higher brain function (memory, judgement, emotion, and thinking) ■ Sensory receptor and signal transduction (receptor and pathway of visual, auditory, and cutaneous senses) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
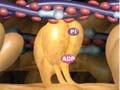
• WT-03 Mechanism of Voluntary Movement |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
■ Motor organ (functions of muscular, skeletal, and arthral, and mechanisms of muscle contraction, energy) ■ Motor control (motor initiation, planning, order, execution, control: cerebral region, pyramidal tract, extrapyramidal tract, motor memory and acquisition of skill ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• WT-04 Continuity of Life |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
■ Development (growth, maturation, aging, physical and functional alterations) ■ Mechanisms of heredity (species preservation and phenogenetics)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• WT-05 Function of Circulatory System |
|
 |
|
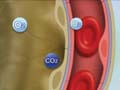 |
 |
■ Blood function: constituents of blood, transport of O2 and CO2 ■ Circulatory system: mechanism of circulation, cardiac pumping ability, vascular function, circulatory regulation ■ Precapillary circulation in tissue: lung-gass exchange, small intestine, lever-absorption or process of nutrient, kidney-excretion of waste product |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• WT-06 Intake and Advantage of Nutrition |
|
 |
|
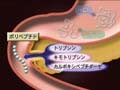 |
 |
■ Three major nutrients: physicality of three major nutrients, digestions and absorptions of glucose and protein, lipid digestion and absorption ■ Digestion: digestion in the oral catity - esophagus, and stomach, function of small intestine, and function of large intestine ■ Nutrient utilization: glucose, lipid -energy, amino acid- protein synthesis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• WT-07 Homeostasis |
|
 |
|
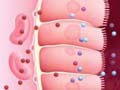 |
 |
■ Homeostasis: internal enviroment - water, electrolyte, glucide, temperature, pH, functions of autonomic nerve and endocrine system ■ Regulation of body fluid: moisture content, regulation of Na concentration, osmoreguation, pH regulation, and acid-base balance ■ Energy regulation: regulation of blood glucose, thermoregulation, and circulatory regulation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• WT-08 Mechanism of Phylaxis |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
■ Mechanisms of detoxication (low molecular weight chemical substance): internal dynamic state, hepatic action- metabolic response, cohesion response ■ Mechanisms of immunity (polymer molecule substance, pathogenic microbe): natural immunity, acquired immunity (intracellular and extracellular growth fungus) ■ Troubles in immune system: allergy, autoimmune disease, graft rejection, and immune deficiency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|









